Comprehensive Bronchitis Treatment and Care
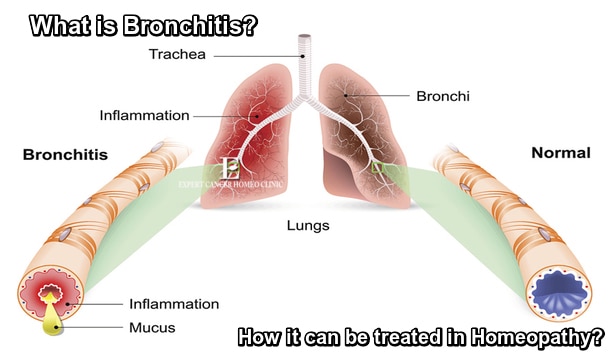
What Is Bronchitis?
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the lining of your bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from your lungs. It is often caused by a viral infection, but can also be triggered by bacterial infections, smoking, or other irritants. Bronchitis can be classified into two types: acute and chronic.
Symptoms of Bronchitis
Common symptoms of bronchitis include:
- Persistent cough with or without mucus
- Shortness of breath or wheezing
- Chest discomfort or tightness
- Fatigue and weakness
- Low-grade fever
- Sore throat and nasal congestion
Causes of Bronchitis
Bronchitis can occur as a result of various factors:
- Viral infections: The common cold or flu viruses are the most common causes of acute bronchitis.
- Bacterial infections: Less common but can contribute to both acute and chronic bronchitis.
- Smoking: Smoking is the leading cause of chronic bronchitis.
- Air pollution: Exposure to dust, fumes, and chemicals can irritate the bronchial tubes.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): Acid reflux can irritate the lungs and lead to bronchitis.
Acute vs. Chronic Bronchitis
There are two main types of bronchitis:
Acute Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is a short-term inflammation that usually lasts for a few weeks. It is commonly caused by viral infections like the cold or flu. Most people recover with rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications.
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition often caused by smoking or exposure to air pollutants. It leads to persistent coughing and can cause significant difficulty breathing over time. It is part of a group of diseases known as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Treatment for Bronchitis
The treatment for bronchitis varies depending on whether it's acute or chronic:
- Acute Bronchitis: Typically, acute bronchitis resolves on its own with rest, hydration, and over-the-counter pain relievers and cough suppressants.
- Chronic Bronchitis: Chronic bronchitis requires long-term management, including smoking cessation, inhalers, and other medications to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
- Antibiotics: If a bacterial infection is identified, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection.
- Airway Clearance Techniques: Inhalers or nebulizers may be used to clear mucus and open up airways for better breathing.
When to Seek Medical Attention
You should consult a doctor if:
- If symptoms last more than three weeks.
- If you experience severe shortness of breath, chest pain, or high fever.
- If you have chronic health conditions, such as asthma or heart disease, that worsen your bronchitis symptoms.
Expert Bronchitis Treatment by Dr. Yashi Singh
Dr. Yashi Singh is dedicated to providing personalized care for bronchitis, whether it's acute or chronic. With years of experience and a compassionate approach, Dr. Singh will work with you to create an effective treatment plan to manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Schedule a Consultation
 +919769194299
+919769194299
